Principle of Solid State Battery
2024-05-11
Principle of solid state battery
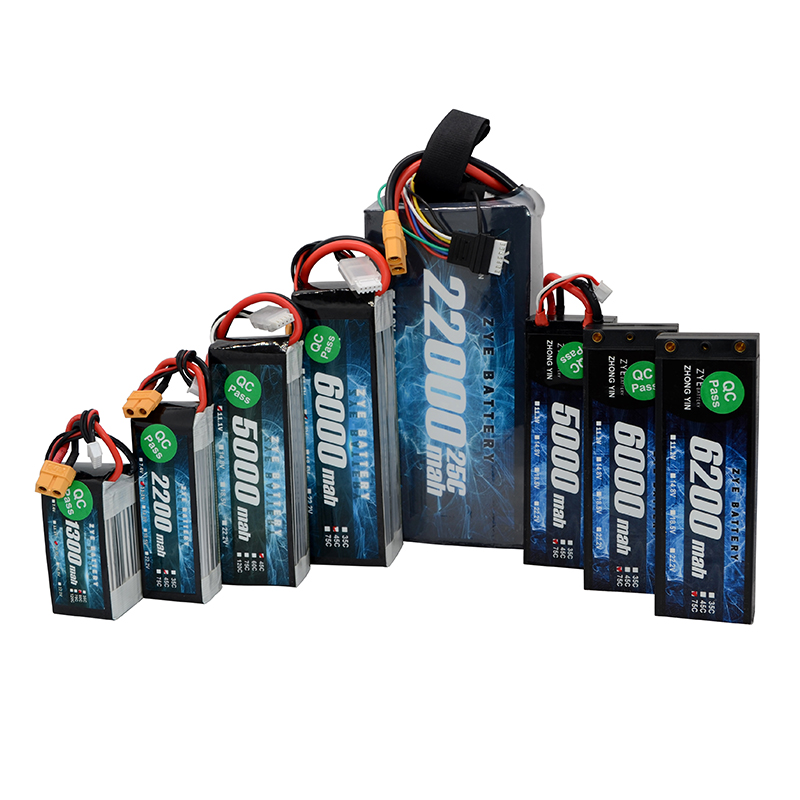
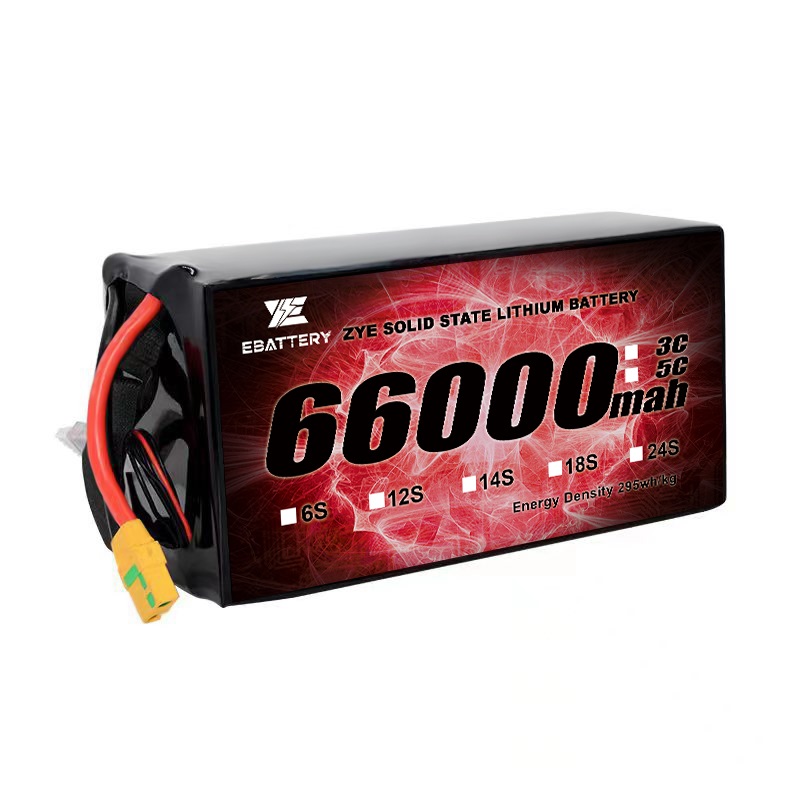
Solid-state batteries are a type of battery technology. Unlike the lithium-ion and lithium-ion polymer batteries commonly used today, a solid-state battery is a battery that uses a solid electrode and a solid electrolyte. Because the scientific community believes that lithium-ion batteries have reached their limits, solid-state batteries have been regarded as batteries that can inherit the status of lithium-ion batteries in recent years. Solid-state lithium battery technology uses glass compounds made of lithium and sodium as conduction substances, replacing the electrolyte of the previous lithium battery, and greatly improving the energy density of the lithium battery.
The traditional liquid lithium battery is also known as the "rocking chair battery" by scientists, the two ends of the rocking chair are the positive and negative poles of the battery, and the middle is the electrolyte (liquid). Lithium ions are like excellent athletes, running back and forth at both ends of the rocking chair, and in the movement of lithium ions from positive to negative to positive, the charge and discharge process of the battery is completed.
Solid-state batteries work in the same way, except that the electrolyte is solid and has the density and structure to allow more charged ions to gather at one end and conduct more current, thus increasing the battery capacity. Therefore, the same amount of power, solid-state batteries will become smaller. Not only that, because there is no electrolyte in the solid state battery, the storage will become easier, and when used in large equipment such as automobiles, there is no need to add additional cooling tubes, electronic controls, etc., which not only saves costs, but also effectively reduces weight. Solid-state batteries are a type of battery technology. Unlike the lithium-ion and lithium-ion polymer batteries commonly used today, a solid-state battery is a battery that uses a solid electrode and a solid electrolyte. Because the scientific community believes that lithium-ion batteries have reached their limits, solid-state batteries have been regarded as batteries that can inherit the status of lithium-ion batteries in recent years. Solid-state lithium battery technology uses glass compounds made of lithium and sodium as conduction substances, replacing the electrolyte of the previous lithium battery, and greatly improving the energy density of the lithium battery.
The traditional liquid lithium battery is also known as the "rocking chair battery" by scientists, the two ends of the rocking chair are the positive and negative poles of the battery, and the middle is the electrolyte (liquid). Lithium ions are like excellent athletes, running back and forth at both ends of the rocking chair, and in the movement of lithium ions from positive to negative to positive, the charge and discharge process of the battery is completed.
Solid-state batteries work in the same way, except that the electrolyte is solid and has the density and structure to allow more charged ions to gather at one end and conduct more current, thus increasing the battery capacity. Therefore, the same amount of power, solid-state batteries will become smaller. Not only that, because there is no electrolyte in the solid state battery, the storage will become easier, and when used in large equipment such as automobiles, there is no need to add additional cooling tubes, electronic controls, etc., which not only saves costs, but also effectively reduces weight.