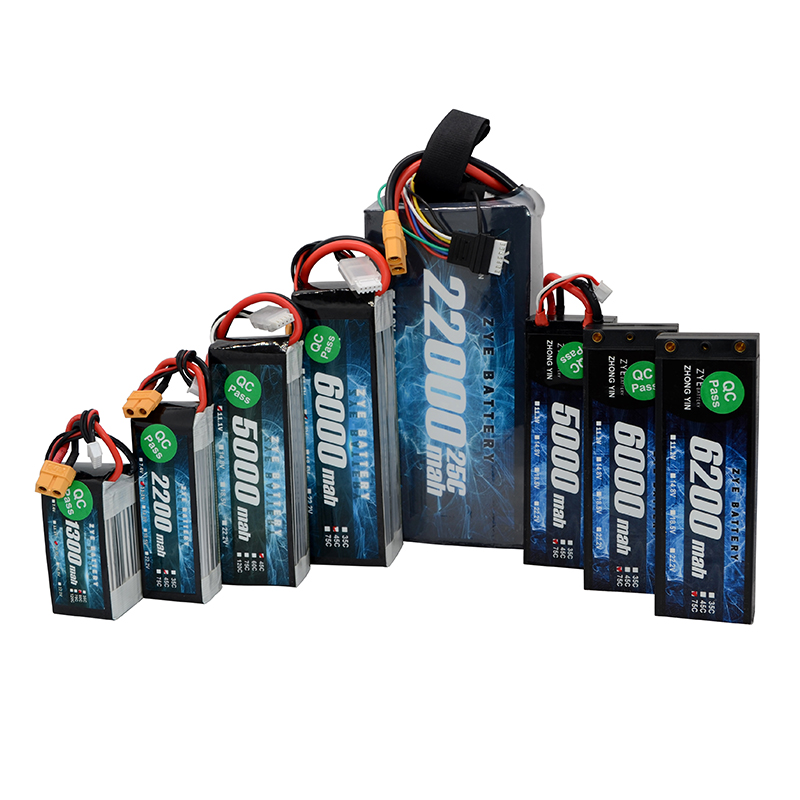
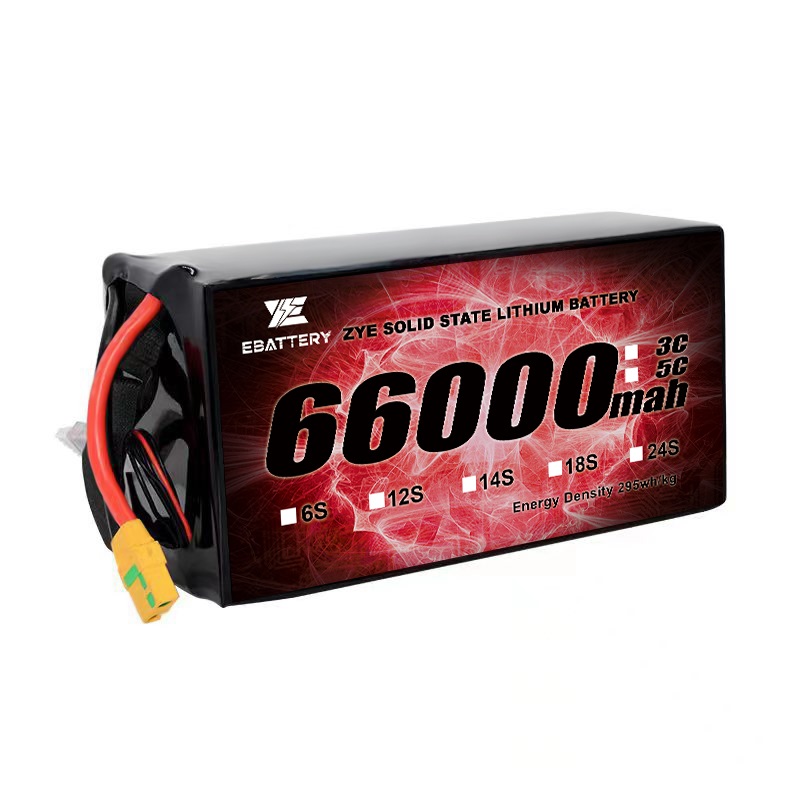
The Drone Solid-state Batteries for Cold Weather Flights
2025-11-28
Severe cold weather has always been a serious challenge to the performance and reliability of unmanned aerial vehicles. Low temperatures can significantly reduce the chemical activity of traditional batteries, leading to a sharp decline in battery life, voltage drops, and even sudden power outages, putting critical flight missions at risk. Semi-Solid State batteries - are offering us a brand-new solution to overcome the severe cold.
Why is low temperature the "archenemy" of traditional drone batteries?
The predicament of traditional lithium polymer (LiPo) batteries at low temperatures:
Low temperatures can significantly affect the performance of drone batteries, leading to shortened flight times and potentially impacting your mission.
Electrolyte solidification: At low temperatures, the liquid electrolyte inside the battery becomes viscous or even partially solidifies, greatly hindering the movement speed of lithium ions.
A sharp increase in internal resistance: The obstruction of ion movement directly leads to an increase in the internal resistance of the battery. To maintain flight, the battery voltage will drop sharply (voltage sag), triggering the low battery protection mechanism of the drone and forcing the aircraft to land earlier.
Severe capacity degradation: In a 0°C environment, the available capacity of traditional LiPo batteries may decrease by 30% to 50%. At even more extreme low temperatures, the performance loss is even more astonishing.
Charging hazard: Charging batteries at low temperatures can cause lithium metal to leach out, which may permanently damage the battery and pose a risk of short circuit and fire.

Solid state batteries, as a transitional technology, ingeniously integrate the advantages of traditional liquid batteries and all-solid batteries. The core lies in mixing electrode materials with solid electrolytes and a small amount of electrolyte to form a semi-solid matrix similar to a gel-like substance.
Solid-State batteries are moving from the laboratory to the forefront of applications. So, how exactly does this highly anticipated technology work? How will it change the future of drones?
The working process of solid-state batteries is macroscopically similar to that of lithium-polymer batteries, still involving the migration of lithium ions between the positive and negative electrodes. However, the implementation methods at the micro level bring about a world of difference.
Solid electrolytes: They are usually made of special solid materials such as ceramics, sulfides or polymers. These materials have extremely high ionic conductivity, allowing lithium ions to pass through quickly while also insulating electrons, perfectly combining the two major functions of conduction and isolation.

Work process
When a battery is charged or discharged, lithium ions (Li⁺) move back and forth between the positive and negative electrodes under the influence of an electric field through the solid electrolyte, which serves as a solid "bridge". Electrons (e⁻) flow through the external circuit, thereby forming an electric current to power the unmanned aerial vehicle.
One of the key challenges in solid-state battery design, regardless of the type of solid electrolyte used, is to optimize the interface between the electrolyte and the electrode. Unlike liquid electrolytes that are easy to adhere to electrode surfaces, solid electrolytes need to be carefully designed to ensure good contact and efficient ion transfer.
ZYEBATTERY has always been focused on cutting-edge energy technologies. We closely follow the development of next-generation technologies such as solid-state batteries and are committed to providing the market with safer and more powerful drone power solutions in the future, helping our customers fly higher, farther and more safely.