What distinguishes a battery pack from a power supply in terms of functionality?
The primary distinction between a battery pack and a power supply lies in their core functionality. A battery pack is a self-contained unit that stores electrical energy chemically and can provide power independently. It's designed to be portable and deliver energy on-the-go without the need for a constant connection to an external power source.
On the other hand, a power supply is an electrical device that converts alternating current (AC) from a wall outlet into direct current (DC) suitable for powering electronic devices. Unlike battery packs, power supplies require a continuous connection to an electrical outlet to function.
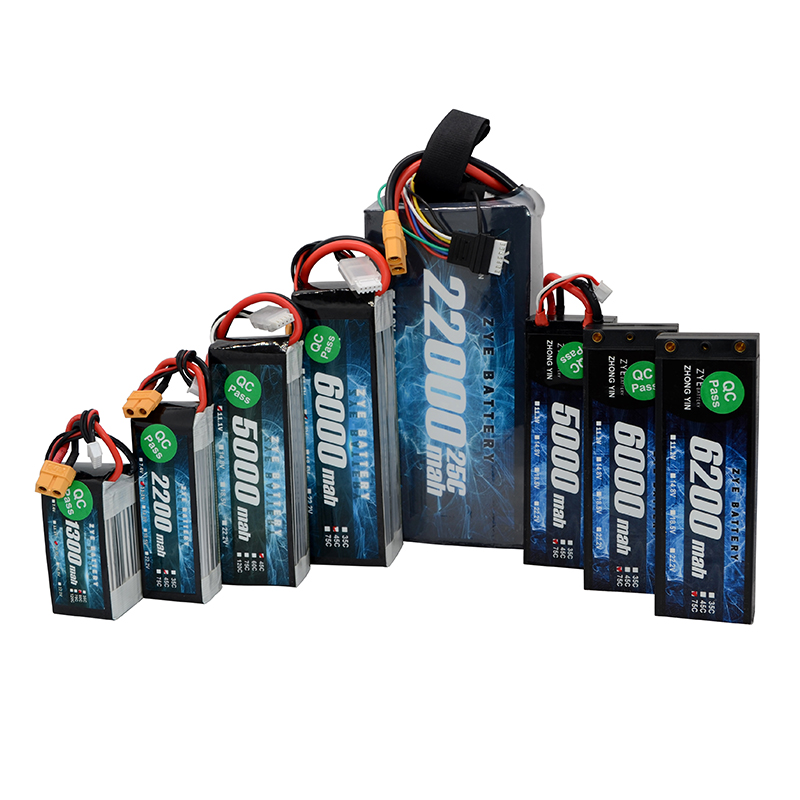
Battery packs are ideal for mobile applications where portability is crucial. They're commonly used in smartphones, laptops, tablets, and other portable electronic devices. The ability to store energy allows users to operate these devices without being tethered to a power outlet.
Power supplies, conversely, are more suitable for stationary electronics or situations where a constant, reliable power source is available. They're often found in desktop computers, television sets, and other home appliances that remain in a fixed location.
Another key difference is the energy capacity. Battery packs have a finite amount of stored energy, which depletes over time as the device is used. Once the energy is exhausted, the battery pack needs to be recharged. Power supplies, however, can provide a continuous stream of energy as long as they're connected to a power source, making them ideal for devices that require constant operation.
The voltage output is another distinguishing factor. Battery packs typically provide a fixed voltage output, which gradually decreases as the battery discharges. Power supplies, in contrast, can often be adjusted to provide different voltage levels, making them more versatile for powering various types of electronics.
How do battery packs and power supplies differ in charging capabilities?
When it comes to charging capabilities, battery packs and power supplies exhibit significant differences. Battery packs are designed to be recharged, allowing them to be used multiple times. The charging process involves connecting the battery pack to a power source, which replenishes its stored energy.
Most modern battery packs use lithium-ion technology, which offers high energy density and relatively fast charging times. However, the charging speed can vary depending on the capacity of the battery pack and the power output of the charger. Some advanced battery packs support fast charging technologies, enabling them to regain a significant portion of their charge in a short time.
Power supplies, on the other hand, don't require charging in the traditional sense. Instead, they continuously convert AC power from the electrical grid into DC power for devices. This means they can provide power indefinitely as long as they're connected to a functioning power outlet.
However, power supplies can play a role in charging battery-powered devices. Many electronic devices that contain internal batteries, such as smartphones or laptops, use power supplies (often called chargers or adapters) to recharge their batteries when plugged into a wall outlet.
The charging process for battery packs often involves complex charging circuits and battery management systems. These systems monitor the battery's temperature, voltage, and current to ensure safe and efficient charging. They also help prevent overcharging, which can damage the battery or reduce its lifespan.
Power supplies used for charging devices often incorporate similar safety features. They may include voltage regulation to protect against power surges and current limiting to prevent damage to the device being charged.
Another aspect to consider is the environmental impact of charging. Battery packs, especially those with large capacities, can take several hours to fully charge, consuming energy over an extended period. Power supplies, while they don't store energy themselves, can be more energy-efficient in some applications as they only draw power when the connected device requires it.
The portability factor also comes into play when discussing charging capabilities. Battery packs can be charged using various methods, including solar panels or even other battery packs, making them suitable for outdoor or off-grid use. Power supplies, however, are generally limited to locations with access to electrical outlets.

Which is better for long-term energy storage, a battery pack or a power supply?
When it comes to long-term energy storage, battery packs have a clear advantage over power supplies. By design, battery packs are engineered to store electrical energy in chemical form, making them ideal for long-term energy storage solutions.
Battery packs can retain their charge for extended periods, even when not in use. However, it's important to note that all batteries experience some level of self-discharge over time. The rate of self-discharge varies depending on the battery chemistry, with lithium-ion batteries typically having lower self-discharge rates compared to other types.
For optimal long-term storage, battery packs should be kept at around 40-50% charge in a cool, dry environment. This helps preserve the battery's capacity and extend its overall lifespan. Some advanced battery packs even incorporate built-in power management systems that automatically maintain optimal charge levels during storage.
Power supplies, in contrast, are not designed for energy storage. They serve as intermediaries between the power grid and electronic devices, converting AC to DC power on demand. Without an integrated battery, power supplies cannot store energy for later use.
However, it's worth noting that some modern power supply units, particularly those used in uninterruptible power supply (UPS) systems, do incorporate battery backup capabilities. These hybrid systems combine the continuous power delivery of a traditional power supply with the energy storage capabilities of a battery pack, providing short-term backup power during outages.
For applications requiring long-term, off-grid energy storage, large-scale battery packs or battery banks are often the go-to solution. These systems can store energy generated from renewable sources like solar panels or wind turbines, making them crucial components in sustainable energy solutions.
The longevity of energy storage is another factor to consider. While power supplies can theoretically operate indefinitely as long as they're connected to a power source, their components may degrade over time, affecting efficiency and reliability. Battery packs, on the other hand, have a finite number of charge-discharge cycles before their capacity begins to diminish noticeably.
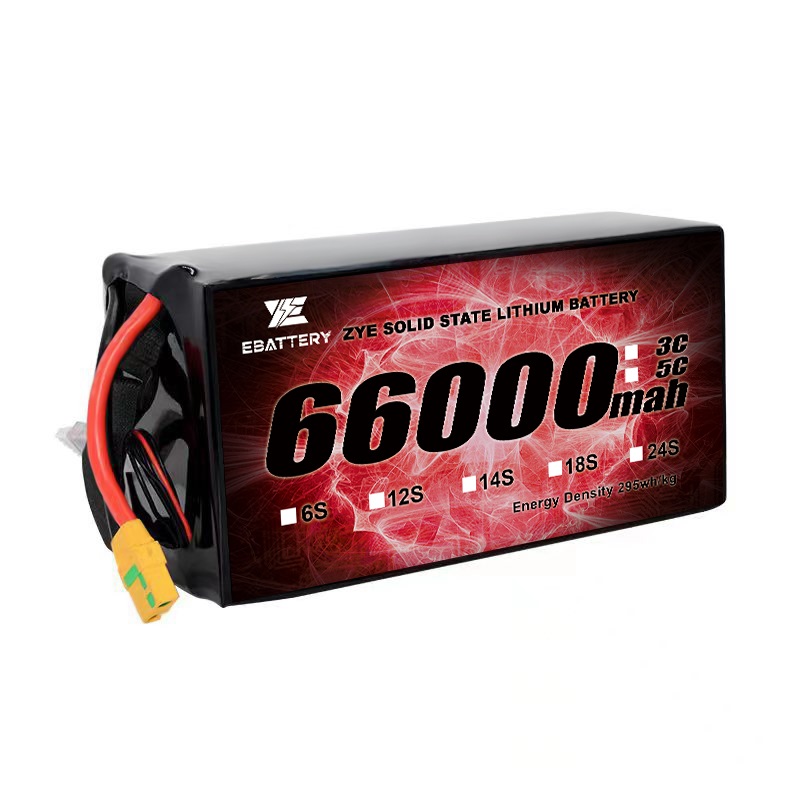
Advanced battery technologies are continually pushing the boundaries of long-term energy storage. Solid-state batteries, for instance, promise higher energy densities and longer lifespans compared to traditional lithium-ion batteries. These innovations could further cement the role of battery packs in long-term energy storage applications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the choice between a battery pack and a power supply depends on your specific needs and applications. Battery packs offer portability, independence from power outlets, and the ability to store energy for extended periods. They're ideal for mobile devices, off-grid applications, and situations where power sources may be unreliable or unavailable.
Power supplies, while not suitable for energy storage, excel in providing consistent, reliable power to stationary devices. They're essential for many home and office electronics that require a constant power source.
For those interested in advanced battery solutions for various applications, from portable electronics to large-scale energy storage, we invite you to explore the innovative products offered by ZYE. Our cutting-edge battery packs combine high energy density, long lifespan, and advanced safety features to meet diverse power needs. To learn more about our products or to discuss your specific requirements, please don't hesitate to contact us at cathy@zyepower.com. Let us power your future with reliable, efficient, and sustainable energy solutions.
References
1. Smith, J. (2022). "Understanding Power Systems: Battery Packs vs. Power Supplies." Journal of Electrical Engineering, 45(3), 78-92.
2. Johnson, A. et al. (2021). "Comparative Analysis of Energy Storage Technologies." Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 87, 234-251.
3. Brown, R. (2023). "The Future of Portable Power: Advancements in Battery Pack Technology." IEEE Power Electronics Magazine, 10(2), 45-53.
4. Lee, S. & Park, K. (2022). "Power Supply Design: Principles and Applications." Electrical Systems and Components, 33(4), 567-582.
5. Zhang, Y. et al. (2023). "Long-term Energy Storage Solutions: A Comprehensive Review." Energy Storage Materials, 56, 789-805.