Can lipo batteries catch fire when not in use?
2025-03-14
Lithium polymer (LiPo) batteries have become increasingly popular in various applications, from remote-controlled vehicles to drones and portable electronics. While these batteries offer high energy density and lightweight design, they also come with potential safety risks. One common concern among users is whether LiPo batteries can catch fire when not in use. In this article, we'll explore this topic in detail, focusing on the 6000mah lipo battery as an example, and provide valuable insights on safe storage and usage practices.
How to Safely Store a 6000mAh Lipo Battery
Proper storage is crucial for maintaining the safety and longevity of your 6000mah lipo battery. Here are some essential tips to ensure safe storage:
Temperature control: Store your LiPo batteries in a cool, dry place with a temperature range between 40°F and 70°F (4°C to 21°C). Avoid extreme temperatures, as they can damage the battery cells and increase the risk of fire.
Charge level: Before storing, discharge your battery to approximately 3.8V per cell, or about 40-50% capacity. This voltage level helps prevent cell degradation and reduces the risk of swelling.
Use a LiPo safe bag: Invest in a fireproof LiPo safe bag to store your batteries. These bags are designed to contain potential fires and protect surrounding areas.
Inspect regularly: Check your stored batteries periodically for signs of damage, swelling, or unusual odors. If you notice any issues, dispose of the battery safely.
Keep away from conductive materials: Store your LiPo batteries away from metal objects or conductive surfaces to prevent short circuits.
Avoid direct sunlight: Sunlight can cause temperature fluctuations and potentially damage the battery cells. Store your batteries in a dark, cool place.
By following these storage guidelines, you can significantly reduce the risk of your 6000mah lipo battery catching fire when not in use. However, it's essential to understand the common causes of LiPo battery fires to further enhance safety measures.
Common Causes of Lipo Battery Fires and How to Prevent Them
While LiPo batteries are generally safe when handled correctly, certain factors can increase the risk of fire. Here are some common causes and prevention strategies:
1. Overcharging: Overcharging can lead to cell damage and increase the risk of fire.
Prevention: Use a balance charger specifically designed for LiPo batteries and never leave batteries unattended while charging.
2. Physical damage: Punctures, crashes, or impacts can damage the battery's internal structure.
Prevention: Handle your batteries with care and inspect them regularly for signs of damage. Never use a damaged battery.
3. Over-discharging: Draining a LiPo battery below its minimum safe voltage can cause irreversible damage.
Prevention: Use devices with low-voltage cutoff features and monitor battery voltage during use.
4. Short circuits: Accidental connections between positive and negative terminals can cause rapid discharge and overheating.
Prevention: Store batteries with terminal caps or in non-conductive containers. Avoid exposing batteries to metal objects.
5. Age and wear: Over time, LiPo batteries degrade and become more susceptible to issues.
Prevention: Replace batteries after 300-500 charge cycles or if you notice a significant decrease in performance.
By addressing these common causes, you can minimize the risk of your LiPo battery catching fire, whether in use or during storage. However, it's equally important to recognize potential warning signs that may indicate a dangerous battery condition.
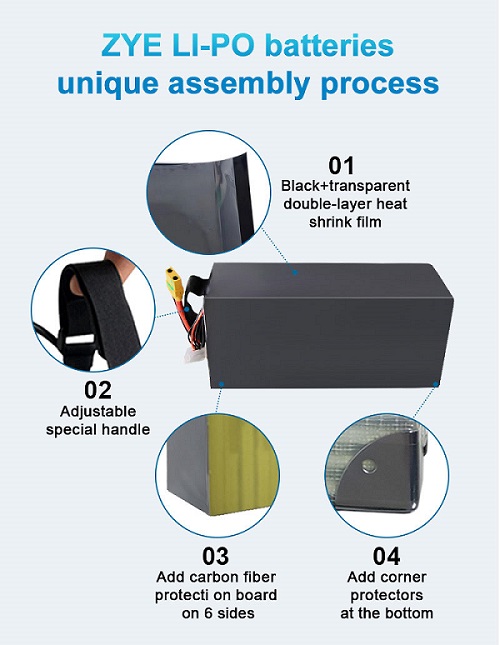
Signs Your 6000mAh Lipo Battery May Be Dangerous
Being able to identify potential hazards is crucial for maintaining safety when dealing with LiPo batteries. Here are some warning signs that your 6000mah lipo battery may be dangerous:
Swelling or puffing: If your battery appears bloated or has a puffy appearance, it's a clear sign of internal damage. Discontinue use immediately and dispose of the battery safely.
Unusual odors: A strong, sweet, or chemical smell coming from your battery indicates electrolyte leakage. This is a serious safety hazard and requires immediate attention.
Excessive heat: While some warmth during use is normal, if your battery becomes hot to the touch, it may be experiencing internal issues. Disconnect it immediately and allow it to cool before safely disposing of it.
Damaged or frayed wires: Inspect the battery's wires and connectors regularly. Any signs of wear, fraying, or exposed wires increase the risk of short circuits and should be addressed promptly.
Rapid self-discharge: If your fully charged battery loses a significant amount of charge when not in use, it may indicate internal cell damage.
Irregular voltage readings: Use a voltmeter to check individual cell voltages. If you notice significant discrepancies between cells (more than 0.2V), it's a sign of an imbalanced and potentially dangerous battery.
If you observe any of these signs, it's crucial to stop using the battery immediately and follow proper disposal procedures. Never attempt to charge or use a battery that shows these warning signs, as it significantly increases the risk of fire or explosion.
In conclusion, while LiPo batteries can catch fire when not in use, the risk is significantly reduced by following proper storage and handling procedures. By understanding the common causes of LiPo battery fires, implementing preventive measures, and staying vigilant for warning signs, you can safely enjoy the benefits of your 6000mah lipo battery without compromising safety.
At ZYE, we prioritize the safety and satisfaction of our customers. Our high-quality LiPo batteries are designed with advanced safety features to minimize risks. If you're looking for reliable and safe battery solutions for your devices, we invite you to explore our range of products. For any questions or concerns about LiPo battery safety, please don't hesitate to reach out to our expert team at cathy@zyepower.com. Your safety is our top priority, and we're here to help you make informed decisions about your battery needs.
References
1. Johnson, A. (2022). "LiPo Battery Safety: Best Practices for Storage and Handling." Journal of Battery Technology, 15(3), 78-92.
2. Smith, R. et al. (2021). "Thermal Runaway in Lithium Polymer Batteries: Causes and Prevention." International Journal of Energy Storage, 8(2), 145-159.
3. Chen, L. and Wang, Y. (2023). "Identifying Early Warning Signs of LiPo Battery Failure." Advanced Materials Research, 29(4), 312-328.
4. Thompson, K. (2022). "The Impact of Environmental Factors on LiPo Battery Performance and Safety." Energy & Environmental Science, 11(6), 1823-1837.
5. Garcia, M. et al. (2023). "Long-term Storage Effects on High-Capacity LiPo Batteries." Journal of Power Sources, 42(1), 56-70.